Ayurvedic Name: Shataru
Description:
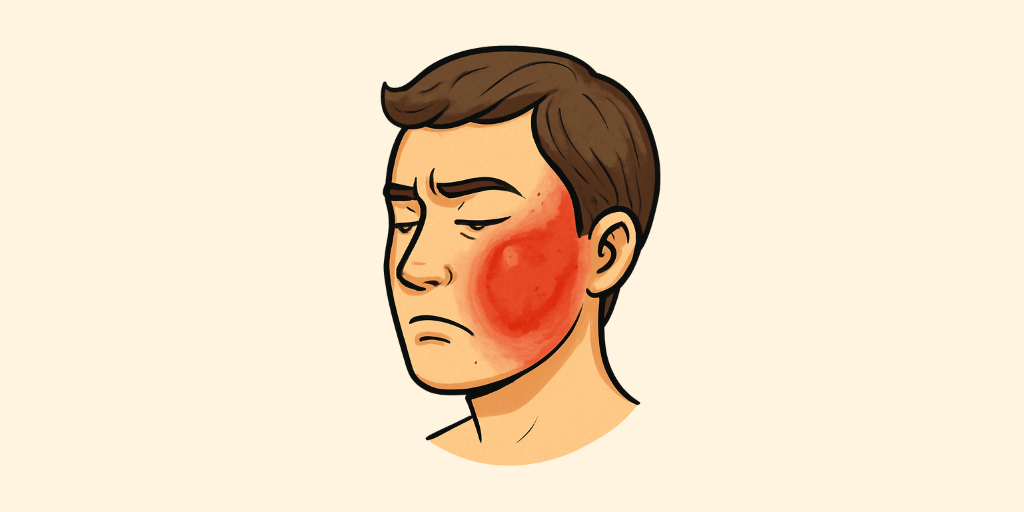
It appears as sharp, painful, red patches with inflammation that spread rapidly, causing burning and severe discomfort. It is a Pitta-Rakta disorder, similar to Cellulitis or Erysipelas in modern dermatology. Ayurvedic treatment includes Gandhak Rasayana, Avipattikar Churna, and cooling applications like Chandan (Sandalwood) and Aloe Vera gel to reduce inflammation.
Signs & Symptoms:
Shataru presents with Kushta (Skin Lesions), Shotha (Swelling), Rukshata (Dryness), Kandu (Itching), and Shoola (Pain).
Diagnosis:
Clinical Diagnosis or Skin Biopsy
Risk Factors:
- Dietary Factors: Consuming excessive amounts of processed foods, sugar, and alcohol can weaken the immune system and increase the likelihood of Shataru (cognitive dysfunction). A poor diet low in nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants can affect mental clarity.
- Lifestyle Factors: Stress, mental exhaustion, and lack of proper sleep can lead to cognitive decline. Sedentary behavior and poor social interaction can also contribute to worsening symptoms.
Complications:
- Skin Scaling (Shataru): Thick, scaly skin patches due to prolonged infection or poor circulation.
- Dryness (Twak Rukshata): Skin becomes dry and cracked due to infection or internal imbalances.
- Itching (Kandu): Persistent itching in the affected skin areas.
Epidemeology:
Shataru (Skin Scaling) is often seen in individuals with psoriasis or eczema, leading to dry, flaky skin. It is more common in those with autoimmune disorders or skin sensitivities.