Ayurvedic Name: Moorcha
Description:
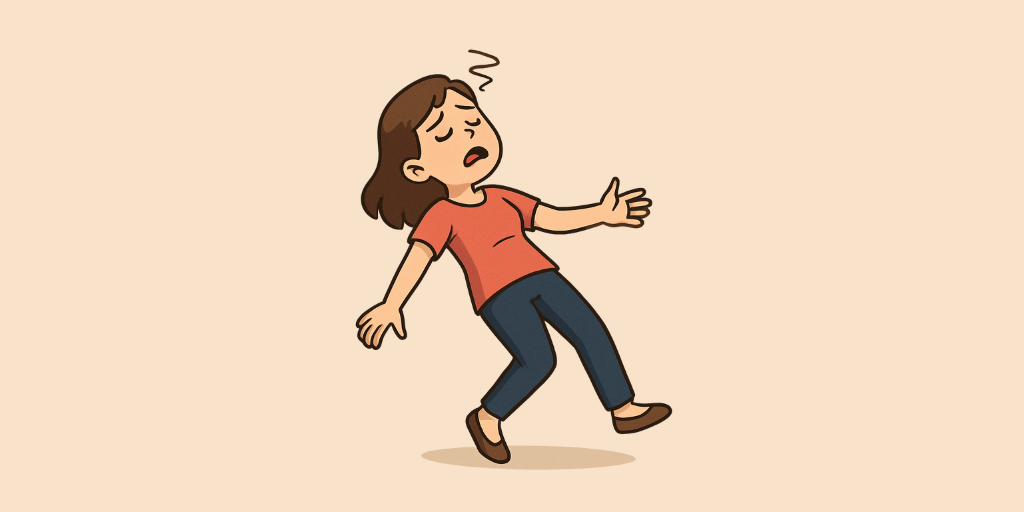
Moorcha refers to fainting or temporary loss of consciousness. It results from sudden imbalances in Vata and Pitta doshas, often due to dehydration, low blood pressure, or excessive heat in the body. Ayurvedic management includes cooling therapies, hydration, and herbal formulations like Shatavari and Ashwagandha.
Signs & Symptoms:
- Murccha (Fainting / Temporary Loss of Consciousness): Sudden loss of consciousness with a feeling of weakness.
- Vata Dosa: Vāta disturbance leads to a feeling of dizziness, leading to fainting.
- Pitta Dosa: Aggravated Pitta can cause overheating, leading to fainting.
- Kapha Dosa: Kapha imbalance contributes to sluggish circulation, leading to fainting spells.
Diagnosis:
Tilt Table Test
Risk Factors:
- Dietary Factors: Consumption of intoxicating foods, alcohol, or excessive amounts of sugary or fatty foods can disturb the nervous system and lead to Moorcha (fainting). A lack of balanced nutrients or hydration can also contribute to dizziness and weakness.
- Lifestyle Factors: High stress levels, emotional trauma, and lack of sleep can trigger Moorcha. Physical exhaustion or dehydration due to excessive heat or strenuous activity can also lead to fainting episodes and dizziness, especially during physical activity.
Complications:
- Fainting (Moorcha): Sudden loss of consciousness due to weak circulation or energy depletion.
- Weakness (Durbalata): Extreme fatigue leading to dizziness or fainting.
- Low Blood Pressure (Tandrata): A drop in blood pressure causing dizziness and risk of fainting.
Epidemeology:
Moorcha (Fainting) is a temporary loss of consciousness usually caused by a sudden drop in blood pressure. It is common in individuals with low blood pressure, dehydration, or blood sugar imbalances. Young adults and older individuals are more susceptible, and fainting episodes can also be triggered by stress, overheating, or standing up too quickly. Frequent fainting may indicate underlying heart or neurological conditions.