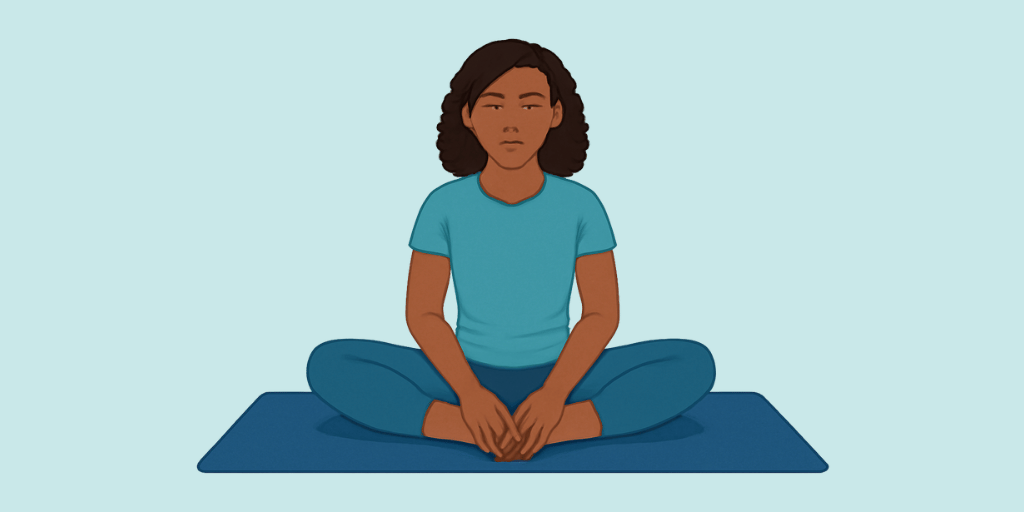
Sanskrit Name: भद्रासन
English Name: Gracious Pose
Description:
Bhadrasana, known as the “Gracious Pose” or “Auspicious Pose,” represents tranquility, stability, and inner peace. The term Bhadra (भद्र) signifies graciousness and auspiciousness, while Asana (आसन) refers to pose or posture. This ancient yoga posture is highlighted in classical texts such as the Hatha Yoga Pradipika and the Gheranda Samhita, where it is regarded as a vital meditative position. Traditionally, sages and yogis employed this pose for extended meditation due to its capacity to enhance stillness and concentration. While it resembles Butterfly Pose (Baddha Konasana), Bhadrasana has the feet positioned slightly farther from the groin. It is commonly practiced across various styles of Hatha Yoga, Kundalini Yoga, and Buddhist meditation. Additionally, Bhadrasana is thought to facilitate the upward flow of prana (life force energy), promoting spiritual awakening and aiding in the balance of the Muladhara (Root Chakra), which relates to grounding and stability.
Benefits:
Bhadrasana, or the “Gracious Pose,” offers several therapeutic benefits, including:
- Improves Flexibility: This asana helps to stretch and open the hips, groin, and thighs, enhancing overall flexibility in these areas.
- Strengthens Pelvic Muscles: Regular practice can strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, which is beneficial for reproductive health and stability.
- Promotes Circulation: Sitting in this pose encourages blood flow to the lower body, which can help alleviate discomfort from sedentary lifestyles.
- Reduces Stress and Anxiety: The grounding nature of Bhadrasana can promote relaxation, reducing stress and anxiety levels.
- Enhances Digestion: The posture aids in stimulating the digestive organs, potentially improving digestion and alleviating constipation.
- Balances Energy: This asana is believed to balance the root chakra, promoting a sense of grounding and stability.
- Supports Meditation: Bhadrasana is often used as a meditative posture, helping practitioners to maintain focus and calm the mind during meditation.
Medical Conditions(Relief):
These benefits make Bhadrasana a valuable addition to any yoga practice, contributing to both physical and mental well-being. Bhadrasana, or the Gracious Pose, can be beneficial for various medical conditions, including:
- Anxiety and Stress: This pose promotes relaxation and helps calm the mind, making it effective for managing anxiety and stress levels.
- Hip Flexibility: Bhadrasana stretches and opens the hips, which can alleviate discomfort associated with tight hip muscles.
- Digestive Issues: By encouraging proper posture and alignment, this asana aids in digestion and can help relieve bloating and discomfort.
- Menstrual Discomfort: The gentle opening of the hips and pelvis can provide relief from menstrual cramps and improve circulation in the lower abdomen.
- Sciatica: Regular practice can help reduce tension in the lower back and improve mobility, offering relief to those suffering from sciatica.
- Posture Improvement: Bhadrasana encourages better spinal alignment, which can be beneficial for individuals with poor posture.
- Mental Clarity: Practicing this pose can enhance focus and mental clarity, making it useful for those experiencing mental fatigue.
By incorporating Bhadrasana into a regular routine, individuals may find relief and improvement in these various conditions.
Medical Conditions(Avoid):
Bhadrasana, or the “Gracious Pose,” is generally beneficial, but certain medical conditions may necessitate avoidance. Here are the conditions to consider:
- Knee Injuries: Individuals with knee injuries or chronic knee pain should avoid this pose as it may exacerbate discomfort.
- Hip Issues: Those with hip problems, such as arthritis or recent surgeries, may find this pose challenging and should refrain from practicing it.
- Ankle Problems: If there are any issues with the ankles, such as sprains or fractures, Bhadrasana could cause further strain.
- Lower Back Pain: People suffering from severe lower back pain should avoid this pose, as it may put additional pressure on the spine.
- Pregnancy: Pregnant individuals, especially in later trimesters, should avoid this pose unless guided by a qualified instructor.
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any new yoga practice, especially if there are pre-existing conditions.