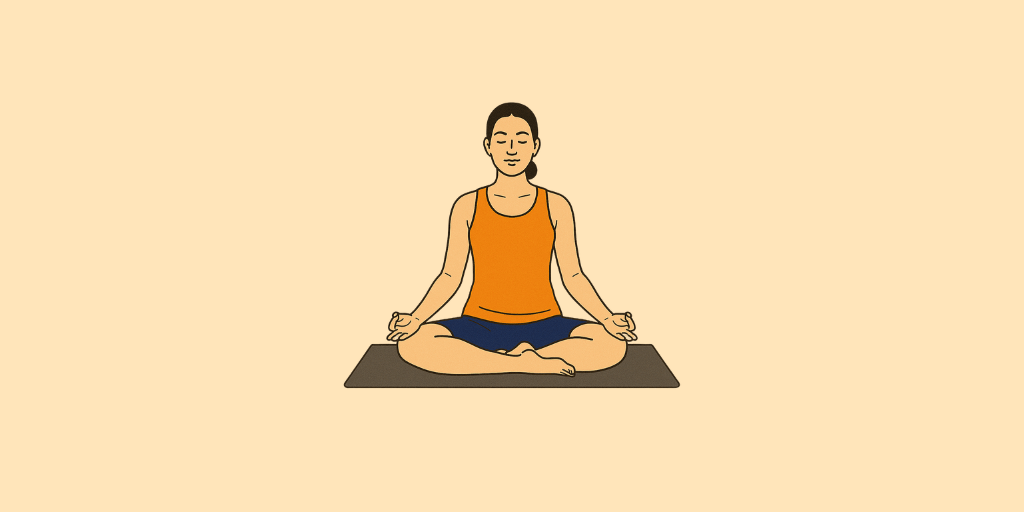
Sanskrit Name: सिद्धासन
English Name: Accomplished Pose
Description:
Siddhasana, also known as the Accomplished Pose, serves as an ideal position for entering a state of deep focus. This seated posture is particularly beneficial for meditation and breathing exercises. In Sanskrit, “Siddha” translates to accomplished or perfected, while “asana” means pose. Thus, Siddhasana symbolizes the “Accomplished Pose” or “Perfect Pose,” embodying the pursuit of balance and mastery in one’s practice—representing the perfect way to sit, remain present, calm, and centered. With its strong roots in Hatha Yoga, Siddhasana is recognized as one of the essential poses for meditation. It is often referred to as the “perfect pose” for meditation due to its ability to foster both physical stillness and mental clarity, providing an optimal position to quiet the mind and eliminate distractions, ultimately creating a serene environment for introspection and connection with one’s thoughts.
Benefits:
- Promotes Meditation: Siddhasana is ideal for meditation, helping to calm the mind and enhance focus.
- Improves Posture: The alignment of the spine in Siddhasana helps improve overall posture and reduce back pain.
- Enhances Circulation: Sitting in this position encourages better blood flow, particularly to the pelvic region.
- Balances Energy: This asana helps balance the body’s energy channels (nadis), promoting overall vitality and well-being.
- Reduces Stress and Anxiety: The meditative aspect of Siddhasana aids in reducing stress and anxiety levels.
- Strengthens the Pelvic Floor: Regular practice can strengthen pelvic muscles, which is beneficial for reproductive health.
- Facilitates Digestion: The seated position can aid in digestion and alleviate gastrointestinal issues.
These benefits make Siddhasana a valuable addition to both physical and mental wellness practices.
Medical Conditions(Relief):
- Anxiety and Stress: Practicing Siddhasana promotes relaxation and helps alleviate symptoms of anxiety and stress by encouraging mindfulness and deep breathing.
- Digestive Issues: This asana aids in improving digestion and can alleviate problems like constipation by stimulating the abdominal organs.
- Sciatica: Siddhasana can help relieve sciatica pain by stretching the lower back and hips, promoting better alignment and reducing discomfort.
- Menstrual Disorders: It may assist in regulating menstrual cycles and reducing associated pain by improving blood circulation in the pelvic area.
- Respiratory Problems: The posture encourages deep breathing, which can enhance lung capacity and improve overall respiratory function.
- Joint Pain: Regular practice can improve flexibility in the hips and knees, which may help ease joint pain and stiffness.
- Insomnia: By calming the mind and body, Siddhasana can be effective in improving sleep quality and reducing insomnia symptoms.
- Mental Clarity: This pose enhances focus and concentration, making it beneficial for those experiencing mental fatigue or lack of clarity.
- Back Pain: Siddhasana helps strengthen the spine and improve posture, which can alleviate chronic back pain over time.
Medical Conditions(Avoid):
- Knee Injuries: Individuals with knee injuries or chronic knee pain may find this posture uncomfortable or exacerbating their condition.
- Hip Issues: Those with hip joint problems, such as arthritis or bursitis, should avoid Siddhasana as it requires significant hip flexibility.
- Back Pain: People suffering from severe or chronic back pain may struggle to maintain proper alignment and could worsen their discomfort.
- Pregnancy: Pregnant individuals should be cautious with this asana, especially in later trimesters, as it can put pressure on the abdomen.
- Recent Surgeries: Anyone who has undergone recent surgeries, particularly in the lower body, should avoid this pose until fully healed.